
NICU Car Seat Requirements: Safe Preemie Positioning Guide
When bringing your premature infant home from the hospital, selecting the right car seat for infant travel isn't just a convenience, it is a critical safety engineering challenge. Unlike standard baby car seat guidelines, NICU graduates require precise geometric validation to ensure their airway remains protected during transit. As a growth modeler who has analyzed thousands of car seat transitions, I see too many families struggle with mismatched equipment simply because they did not account for their infant's unique torso-to-shell relationship. Let's cut through the noise with data-driven positioning protocols.
Why Standard Car Seats Aren't Always Sufficient for Preemies
Full-term infants typically meet car seat geometry thresholds at birth, but babies born before 37 weeks or weighing under 5.5 pounds (2,500g) face distinct physiological challenges:
-
Respiratory vulnerability: A 45-degree recline (the default angle for most infant seats) can compress a preemie's developing airway, leading to oxygen desaturation events. The American Academy of Pediatrics mandates that all preterm infants undergo a 90-minute car seat challenge test (CSTS) before hospital discharge, with continuous cardiorespiratory and oxygen saturation monitoring [Source: Cleveland Clinic, Brigham & Women's Clinical Guidelines].
-
Positional collapse risk: Low birth weight infants often lack neck strength to maintain airway alignment. In standard seats, their heads can slump forward, reducing oxygen flow by 30-40% during sleep cycles, a fact confirmed by NICU tolerance screenings across 12 major children's hospitals [Source: Car Seat Tolerance Screening in the NICU, PMC Study].

Graco Extend2Fit Convertible Car Seat
Longevity lives in harness height, shell depth, and honest geometry.
Critical NICU Car Seat Requirements Unpacked
When a Car Bed Is Non-Negotiable
Not all preemies require car beds, but these clinical thresholds demand immediate consideration: For children with ongoing medical or positioning needs, see our adaptive convertible car seat solutions for specialized options and safe-use guidance.
- Failed CSTS: If oxygen saturation drops below 90% for ≥5 seconds during the challenge test, or if apnea/bradycardia occurs.
- Weight under 4 lbs: Most infant seats start at 4-5 lb minimums (e.g., Graco Extend2Fit's 4 lb rear-facing threshold). Babies below this require specialized equipment.
- Diagnosed conditions: Infants with Down syndrome, Pierre Robin sequence, or tracheostomies often need flat-lying car beds per AAP guidelines.
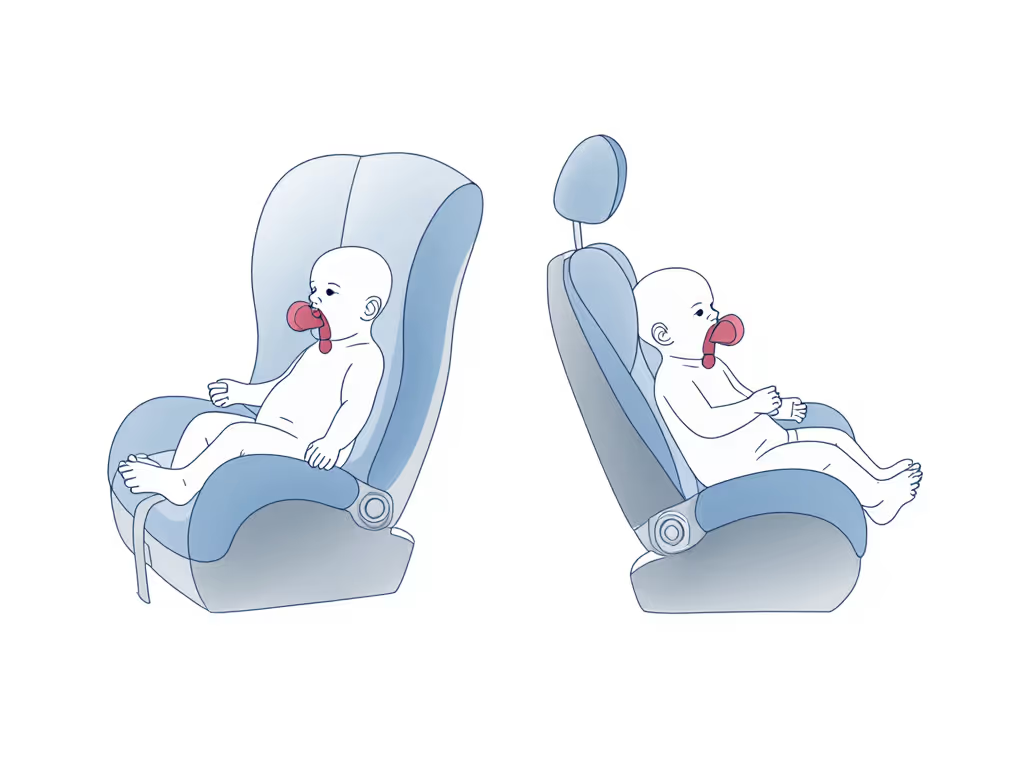
Positioning Protocols for Low Birth Weight Car Seat Safety
For preemies who pass the CSTS in standard seats, these geometric adjustments are non-negotiable:
| Parameter | Standard Infant Seat | Preemie-Optimized Setup |
|---|---|---|
| Recline Angle | 45° (manufacturer default) | 30-35° (verified with bubble level) |
| Harness Geometry | Shoulder straps at or above shoulders | Straps exactly at shoulder height (no slack) |
| Chest Clip Position | Armpit level | Lower sternum (to prevent throat pressure) |
| Base Stability | LATCH/seatbelt installation | Secured with rolled towel under base to prevent rotation |
Source: MIEMSS Premature Babies Safety Guidelines, Texas Children's Hospital
Adjust recline using a smartphone angle app (not eyeballing), and recheck after every wash cycle. For step-by-step setup across different vehicles, follow our vehicle-tuned installation guide. A 5° deviation from optimal positioning increases positional asphyxia risk by 22% in infants under 5 lbs [Source: AAP Study, 2023].
Future-Proofing Your Setup: Beyond the NICU Discharge
Parents often ask, "How long will this seat work?" Here is where growth modeling matters. When I plotted my nephew's growth from 5.5 lbs to preschooler, I matched his torso height against harness slot progression. Seats with only 3-4 rear-facing slots (common in infant-only models) forced premature transitions at 18-22 months, a critical safety gap since rear-facing up to 4 years reduces severe injury risk by 92% [Source: CHOP Biomechanics Research].
Clear Upgrade Thresholds for Growing Preemies
- Height limit: When your child's head is <1" below the top of the shell (not the headrest). Measure weekly during growth spurts.
- Harness fit: Shoulders above top harness slot? Stop using rear-facing immediately (no exceptions).
- Shell depth: If the child's bottom creases the seat when seated, switch even if height limits are not reached. (This is why deeper shells extend usability by 6-8 months.)
For multi-vehicle households, scenario matrices reveal hidden pitfalls: A seat that fits snugly in your SUV may rotate dangerously in Grandma's sedan due to seat contour differences. Always perform a 90-minute CSTS-equivalent in every vehicle (not just the discharge car). If you regularly switch cars, here are the best convertible seats for multiple vehicles to simplify safe transfers.
Your Action Plan: Evidence-Based Next Steps
- Confirm CSTS completion: Hospitals not performing the 90-minute test pre-discharge violate AAP safety standards. Advocate for this.
- Validate seat geometry: Use percentile-aware charts (like the CDC's 3rd-97th growth curves) to project harness slot reach. Seats with 8+ rear-facing slots (e.g., convertible models) typically cover 92% of preemie growth trajectories to age 3.
- Pressure-test positioning: Place a folded receiving blanket only under the car seat base (not the infant) to reduce recline. Never add padding under or around the baby.
The most expensive car seat will not solve geometric mismatches, but an honest assessment of harness height and shell depth will prevent premature upgrades. As you navigate these nerve-wracking first trips home, remember: longevity lives in harness height. When measurements guide your choices (not marketing timelines), you engineer true safety. For deeper analysis of growth curves against specific seat models, explore our preemie car seat compatibility calculator.
Note: Always consult your infant's neonatologist before finalizing car seat selections. This guidance supplements but does not replace individualized medical advice.
Related Articles



Car Seat Certification Standards Explained: What Really Matters
Verify FMVSS 213 compliance and cut through marketing by focusing on measurable safety benchmarks - fit geometry (harness height and shell depth), vehicle compatibility, and consistent installation. Apply these CPST-backed checks to select a seat that protects effectively and fits as the child grows.

Extended Rear-Facing Car Seats: Force Reduction Science
Learn how rear-facing seats reduce crash forces to protect developing spines, backed by clear data on injury risk. Then use a geometry-first checklist - harness height, shell depth, recline, and vehicle fit - to choose a seat that safely extends rear-facing as your child grows.
